
NAME Introduction to Guided Notes 1. Basic Terms
Genetics, otherwise known as the Science of Heredity, is the study of biological information, and how this information is stored, replicated, transmitted and used by subsequent generations. The study of genetics can be sub-divided into three main areas: Transmission Genetics, Molecular Genetics, and Population Genetics. In this Introductory text, the focus is on Transmission or Classical.

Unit 4 Study Guide Chapter 11 Sections 1, 2 & 3 4
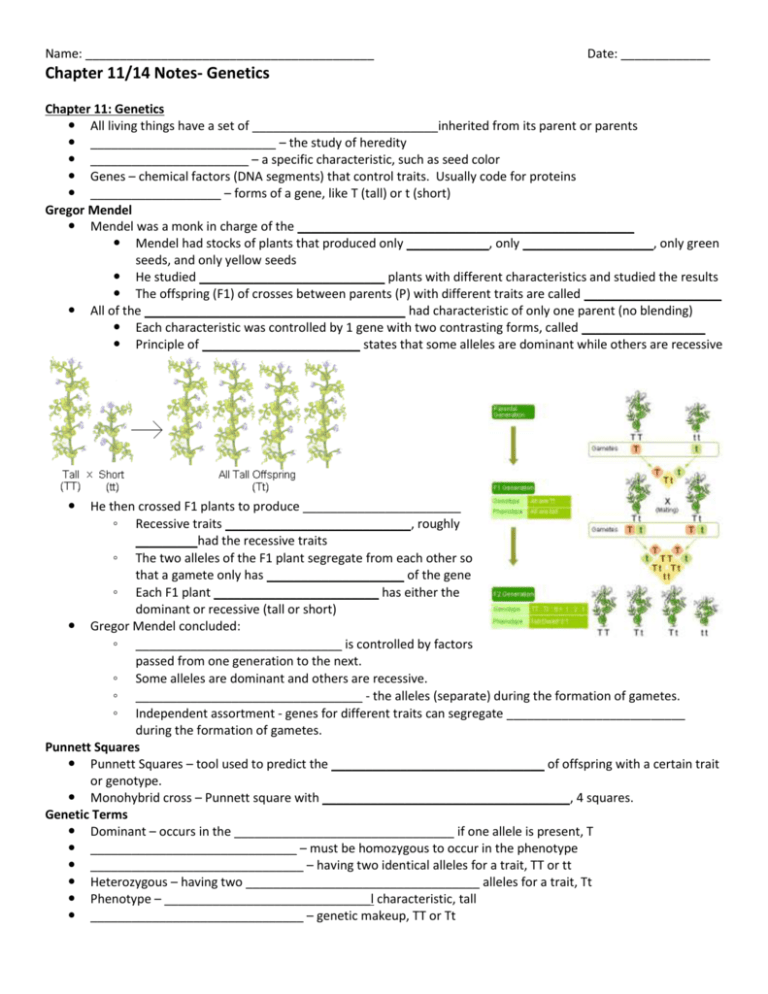
12.1 Mendel's Experiments and the Laws of Probability. 12.2 Characteristics and Traits. 12.3 Laws of Inheritance. Genetics is the study of heredity. Johann Gregor Mendel set the framework for genetics long before chromosomes or genes had been identified, at a time when meiosis was not well understood. Mendel selected a simple biological.

Introduction to
Mendelian Genetics CK 4 Probability and Pedigrees CK 5 Chromosomes and Sex Linkage CK 6 Recombination and Genetic Maps CK 7 Three-factor Crosses CK 8 Tetrad Analysis. notes Lecture Notes. Download Course. Over 2,500 courses & materials Freely sharing knowledge with learners and educators around the world.

Introduction to Lecture notes BIOL1005 Notes 460 eda me Bxpmssxon StuDocu
Introduction to Genetics. "Genetics" is the study of how traits are inherited. A trait is defined as a variation in the physical appearance of a heritable characteristic. It seeks to understand how traits are passed from generation to generation. Before you start learning about the details of inheritance, let's review some topics that are.

PPT SMATH 14 PowerPoint Presentation ID1895736
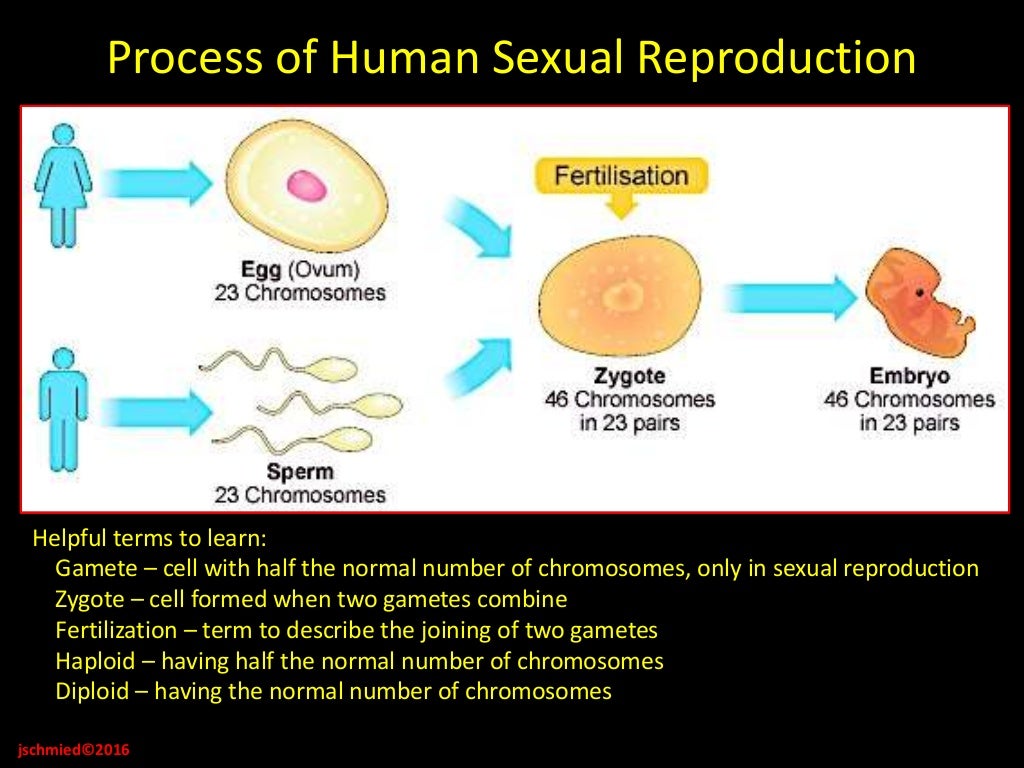
Heredity describes how some traits are passed from parents to their children. The traits are expressed by genes, which are small sections of DNA that are coded for specific traits. Genes are found on chromosomes. Humans have two sets of 23 chromosomes— one set from each parent.

Unit 6 MR. IM Biology
2. Basic model of Quantitative Genetics. Basic model: P = G + E. = average phenotypic value for that genotype if we are able to replicate it over the universe of environmental values, G = E[P] = average value of an inbred line over a series of environments. x E interaction --- The performance of a particular genotype in a particular environment.

Pin on All SHN Products
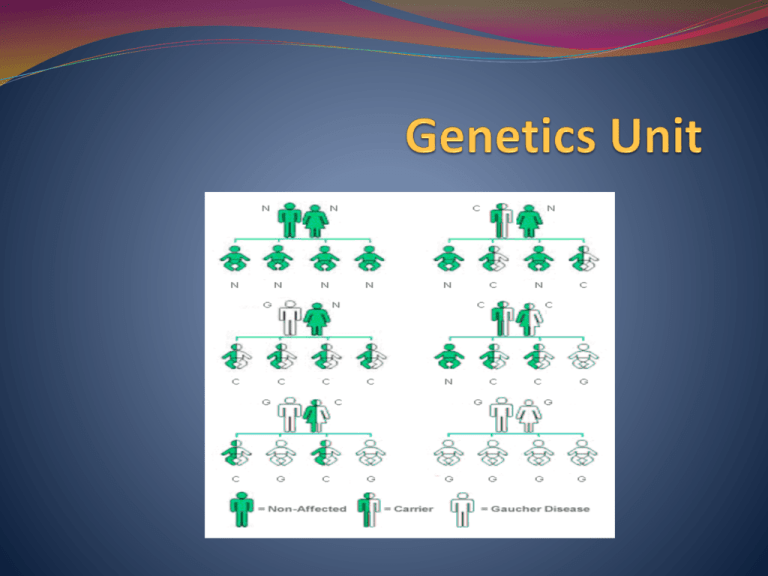
LECTURE 1 - INTRO TO GENETICS - 20% genetic disease - classic Medical genetics, single gene, early onset (pediatric) - 80% genetic susceptibility - common gene variation and environment, delayed onset (adult) Pedigree - Children, siblings, parents - Nuclear family - age/date birth, health status, age/date death, cause of death
unit notes
The passing of traits from parents to offspring is known as heredity, therefore, genetics is the study of heredity. This introduction to genetics takes you through the basic components of genetics such as DNA, genes, chromosomes and genetic inheritance. Genetics is built around molecules called DNA. DNA molecules hold all the genetic.
(PDF) Introduction to Molecular Class Notes for Biotech. 306
Introduction. Figure 18.2 Johann Gregor Mendel is considered to be the father of genetics. Genetics is the study of heredity. Johann Gregor Mendel (1822-1884) set the framework for genetics long before chromosomes or genes had been identified, at a time when meiosis was not well understood ( Figure 18.2 ). Mendel selected a simple biological.

Introduction to A Molecular Approach 1st Edition (Paperback) Routledge
Almost every human trait and disease has a genetic component, whether inherited or influenced by behavioral factors such as exercise. Genetic components can also modify the body's response to environmental factors such as toxins. Understanding the underlying concepts of human genetics and the role of genes, behavior, and the environment is important for appropriately collecting and applying.
Notes
Genetics forms one of the central pillars of biology and overlaps with many other areas, such as agriculture, medicine, and biotechnology. Since the dawn of civilization, humankind has recognized the influence of heredity and applied its principles to the improvement of cultivated crops and domestic animals. A Babylonian tablet more than 6,000.

Notes Introduction to PowerPoint
Introduction to Genetics. Genetics is the study of how genes bring about characteristics, or traits, in living things and how those characteristics are inherited. Genes are specific sequences of nucleotides that code for particular proteins. Through the processes of meiosis and sexual reproduction, genes are transmitted from one generation to.

Introduction to Molecular Lecture Notes StuDocu
A gene is composed of a series of mutable sites that are also sites for recombination (now recognized as nucleotides). One gene encodes one polypeptide. The gene and the polypeptide are colinear. Single amino acids are specified by a set of three adjacent mutable sites; this set is called a codon.

Notes Miller Levine Biology Book (Chapter 11 Sections 1
2. Genetics is central to human affairs (food, health). 3. Genetic information is the basis for every process and structure in an organism. 4. The three main approaches to studying genetics unify the study of biology. 5. The doubling time for general scientific knowledge is 10 years - for genetics 5 years. D. Organization of this class

Is Not So Tough! (An Overview on Interactive Biology, with Leslie Samuel
Figure 19.1.1 19.1. 1: The Central Dogma - DNA is used to make RNA is used to make protein. (CC BY 4.0; OpenStax via Concepts of Biology) Recall that eukaryotic genes are found on chromosomes and that each eukaryotic chromosome typically contains hundreds or thousands of genes. In most eukaryotes, including humans and other animals, each cell.
Notes
Introduction to genetics. Genetics is the study of genes and tries to explain what they are and how they work. Genes are how living organisms inherit features or traits from their ancestors; for example, children usually look like their parents because they have inherited their parents' genes. Genetics tries to identify which traits are.